Scientists:
Principal Investigator: Zlatko Janeba (IOCB Prague). PNP Team (IOCB Prague): Jan Skácel, Michal Česnek, Pavel Kraina, Helena Mertlíková-Kaiserová, Jaroslav Kozák, Pavlína Maloy Řezáčová
Challenge
T-cell leukemias/lymphomas are a clinically heterogenous group of rare, but often aggressive malignancies. Current treatment options for T-cell leukemias/lymphomas are limited, especially for patients who have relapsed after the first-line treatment. The median overall survival for relapsed peripheral T-cell lymphoma has been estimated at ca. 6 months (Mak 2013; DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2012.44.7524).
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) is a ubiquitous enzyme required for purine metabolism. T-cell proliferation is known to be crucially dependent on the PNP activity. Thus, effective PNP inhibition could be beneficial in conditions characterized by malignant T-cell growth. The first (and so far only) marketed PNP inhibitor, forodesine, is currently available only in Japan (as of Jan 2021, brand name Mundesine).
Beside T-cell malignancies, PNP has been proposed as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of bacterial and parasitic infections (Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Plasmodium falciparum).
Technology
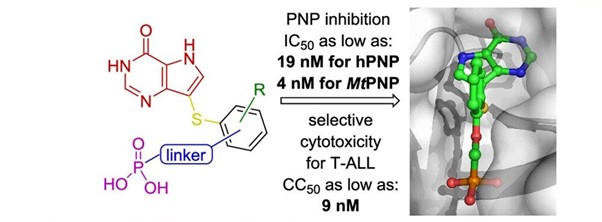
We have designed novel potent inhibitors of the human and bacterial (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) PNP enzyme. Our most potent inhibitors exhibit IC50 values in low nanomolar range for both enzyme subtypes. Cytotoxicity toward various T-lymphoblastic cell lines with CC50 values as low as 9 nM was also observed. The cytotoxic effect was highly selective; other (non-T) cancer cell lines (HeLa S3, HL60, HepG2) and primary peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were unaffected by the treatment (up to 10 μM). The results are further supported by an extensive crystallography study of eight enzyme-inhibitor complexes, elucidating structure activity relationship. Current generation of inhibitors significantly improves ADME properties and activities of the compounds. The ultimate goal is to develop non-ionizable and permeable PNP inhibitors that would enable PNP targeted therapy.
Commercial opportunity
This project is offered for co-development or licensing.
Development status
Lead optimisation
Categories
Enzyme inhibitor; Oncology; Antibacterial
Keywords
purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) T-cell leukemia T-cell lymphoma
Further reading
-
Skácel J, Djukic S, Baszczyňski O, Kalčic F, Bílek T, Chalupský K, Kozák J, Dvořáková A, Tloušt'ová E, Král'ová Z, Šmídková M, Voldřich J, Rumlová M, Pachl P, Brynda J, Vučková T, Fábry M, Snášel J, Pichová I, Řezáčová P, Mertlíková-Kaiserová H, Janeba Z. Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Crystallographic Study of Novel Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase Inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2023 May 25;66(10):6652-6681. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c02097. Epub 2023 May 3. PMID: 37134237; PMCID: PMC10226123.